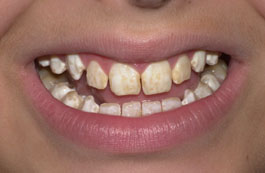
This is a condition affecting the enamel of the permanent front teeth and permanent six year molar teeth. Normal enamel is white and very hard, hypomineralised enamel is creamy, yellow or brown in colour and is chalky in texture. As a result these teeth look different in appearance and are at a higher risk of developing decay .
The cause is not understood but it results from some outside interference during the enamel formation i.e. from birth to four years of age. Respiratory problems, high temperatures and exposure to antibiotics have been put forward as possible causes.
These hypomineralised teeth are often sensitive to cold or brushing.
Management starts with desensitising toothpastes, application of tooth mousse soon after eruption, followed by fissure sealing when fully erupted. If surface breakdown occurs restoration with a filling or crown is indicated. In severe cases, where all the molars are involved extensively, it may be necessary to remove the molars. The best result from a space point of view occurs if the molars are removed at nine to ten years of age. This allows the next molars to slot into the position of the extracted molars. The front teeth may require cosmetic fillings but treatment is often delayed until the teeth are fully erupted. Long term porcelain veneers or crowns may be needed for the front teeth.